OEE, scrap rate and more
Important metrics and KPIs for production
Suitable metrics help with monitoring production processes and identifying problems, weaknesses or optimization potential. In this article, we introduce and explain some of the most important manufacturing metrics.
Definition
What are production metrics?
Production metrics are specific measurements and performance indicators utilized in industrial production. They allow companies to systematically monitor and evaluate selected processes or areas of a production – even within highly complex production environments.
Production metrics can measure a wide range of factors and dimensions, including for example quantity, quality, costs and time. They aid in identifying not only urgent problems but also general optimization potentials. Furthermore, they serve as a means to assess implemented measures and form the basis for (management) decisions.
Many production metrics can be compared not only within a company but also with well-known industry standards.
Key performance indicators (KPIs) are special metrics that measure the achievement of corporate goals. If a certain production metric is of high strategic importance for a company and its maximization or minimization represents an overarching goal, it can be referred to as a production KPI.
Metrics
The most important production metrics
Below, we introduce eight of the most used metrics in industrial production. We explain their corresponding formulas (if any), discuss their significance in various production environments and list opportunities for optimization.
Since modern production environments are not only highly complex but also extremely individualized, not every metric will be useful for every manufacturing company.
For a company that manufactures specific parts for major clients on a short-term basis, delivery reliability and immediate fulfillment of quality standards are of very high importance. On the other hand, companies producing for wholesale tend to more strongly prioritize optimal inventory management.
The following production metrics are explained in this section:
Production volume
The production volume refers to the quantity of goods produced in a certain period of time.
The metric itself is easy to understand, but determining the optimal production volume is very complex and depends on various factors.
Ideally, market demand is optimally met by production. On the other hand, the possible production volume is limited by the available capacities: production facilities, labor and logistics capacities. Cost structures must also be considered.
In practice, particular attention should be paid to ensuring that existing capacities are optimally utilized while trying to avoid overstocking at the same time.
Scrap rate / Reject rate
The scrap rate or reject rate refers to the proportion of defective products out of the total quantity produced.
In some cases, rejects can be reworked into a product that meets quality standards. In other cases, flawed products must be completely sorted out (scrapped) due to certain defects. In textile processing this could be material flaws, in food production it could be spoiled ingredients.
Logically, production companies want to minimize their scrap/reject rate, as it can be associated with high costs. Typical or acceptable scrap/reject rates can vary greatly depending on the industry and the type of products produced.
In industries that manufacture high-precision components, such as semiconductor and electronics production, even minor deviations can lead to a high number of rejects. These industries tend to have relatively high reject rates, but invest heavily in technologies and processes to minimize rejects.
Various measures can be used to minimize rejects:
Data analysis: Recording and evaluation of production data to identify and localize the causes of rejects
Quality control: Implementing strict quality control procedures at various points in the production process
Employee training: Increasing employee proficiency through regular training in quality management practices and the correct handling of machines and materials
Optimization of maintenance strategy: Regular and/or data-driven maintenance (predictive maintenance) to improve precision and avoid machine wear and tear
Optimization of material management: Minimization of material defects through the use of high-quality raw materials/components and an effective inventory management system
Right First Time
Right First Time is a particularly important key figure for companies aiming to reduce costs. It indicates the proportion of products that have no defects in the first production run and therefore require no reworking.
A high value for Right First Time is an indicator of high quality and process efficiency in production. Maximizing the Right First Time KPI not only avoids costs by minimizing scrap and rework, but can also lead to higher customer satisfaction.
The measures for maximizing the Right First Time KPI are largely the same as those for minimizing rejects (see Scrap rate / Reject rate).
Cycle time
The cycle time of a product is the period of time from the start of production (start of the setup process) to the completion (storage, shipment,…) of the product.
The cycle time includes the following factors:
- Set-up times: Preparation of equipment for the production of a specific product
- Waiting times: Periods of time during which the product waits for the next processing step
- Transportation times: Transportation of the product between different stations
- Testing and inspection times: Time for quality or safety checks
To optimize cycle times, the above-mentioned factors should be recorded and optimized separately. Setup times for example can be minimized through more efficient machine allocation.
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE)
Overall Equipment Effectiveness (OEE) is one of the most popular key figures for evaluating equipment productivity. It is made up of several sub-factors and aims to show exactly where productivity losses occur.
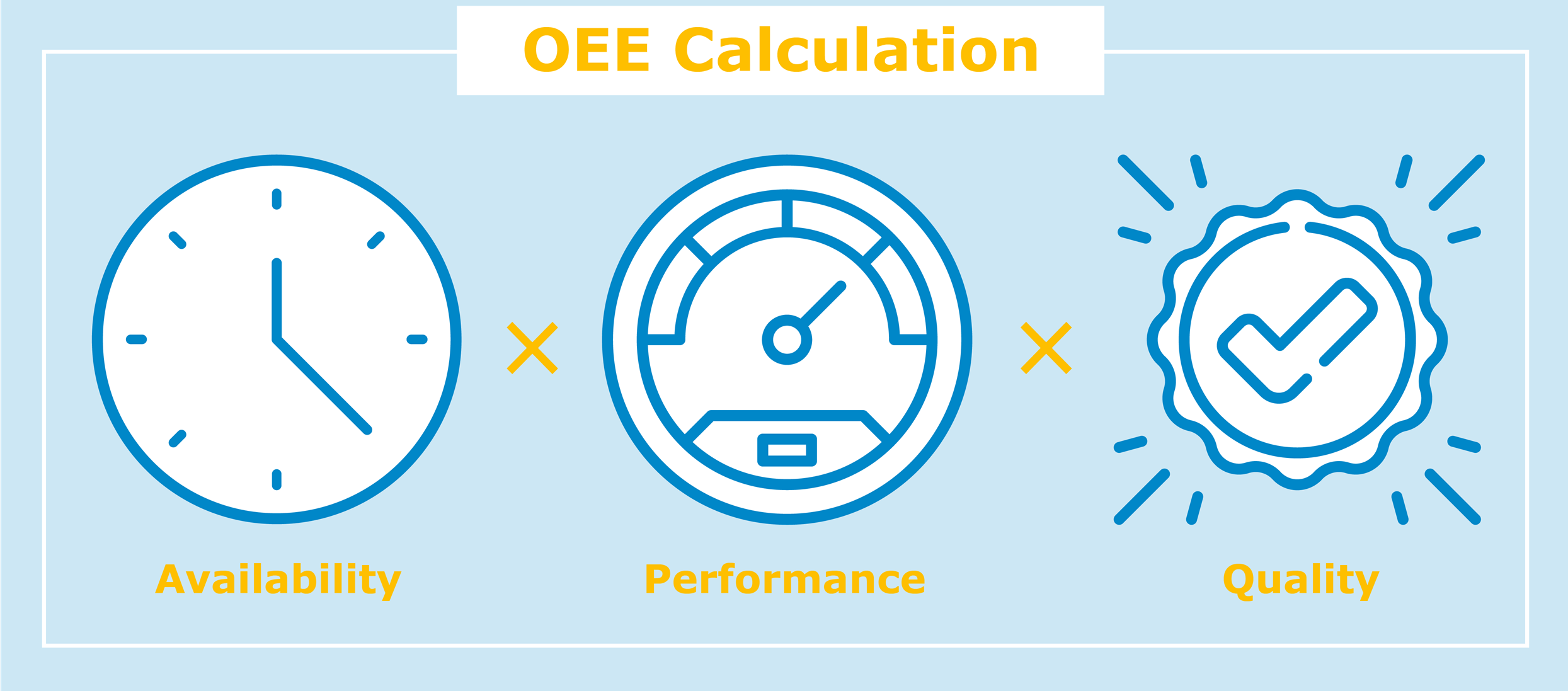
The OEE is given as a percentage and is calculated as follows (usually for a single machine):
OEE = Availability x Performance x Quality
Availability is the ratio of actual production time to planned production time. It is reduced by unplanned downtimes. Performance is the share of the produced quantity in the maximum possible production quantity. The quality factor refers to the proportion of flawless products in the quantity actually produced.
The exact definition and calculation of the individual factors is explained in this article: What is OEE?
Overall Operations Effectiveness (OOE)
Overall Operations Effectiveness (OOE) is similar to OEE. The difference is that OOE extends the scope of efficiency measurement beyond the individual machine or system to the entire operating performance.
While OEE only includes unplanned downtimes in its availability factor, OOE also takes planned downtimes for maintenance, shift changes, etc. into account. These are included in an additional planning factor that extends the typical OEE formula.
The Overall Operations Effectiveness (OOE) is calculated as follows:
OOE = Planning factor x Availability x Performance x Quality
The availability, performance and quality factors are calculated in the same way as for OEE (see What is OEE?). The planning factor describes the proportion of the planned production time to the total production time.
The total production time could be the length of a shift and also includes planned non-production times such as breaks or planned maintenance work.
Inventory turnover rate
The inventory turnover rate is a key logistics figure with major implications for production planning. It measures how often a company turns over or sells its entire stock within a certain period of time (usually 1 year).
The indicator provides information on the efficiency of warehousing and shows how quickly a company sells its products. As the storage of products is associated with costs and ties up capital, companies try to keep their stock levels to a minimum and increase the inventory turnover rate.
This naturally has an impact on production planning. Companies should try to determine the demand for products as accurately as possible and adjust the planned production quantities accordingly. Other measures include eliminating hard-to-sell products and creating greater flexibility in production (e.g. through modern technologies) in order to react quickly to market demand. The implementation of just-in-time production also increases the inventory turnover rate.
A high stock turnover rate can potentially lead to stock shortages. It is therefore important to find a certain balance.
The inventory turnover rate can be calculated using the following formulas:
Stock issues / Average stock level
or
Annual turnover / Average stock level
The average stock level is calculated by adding the opening and closing stock levels for the period in question and dividing by two. Monthly average values can also be used for a more precise calculation:
∑Monthly stock / Number of months
The stock turnover rate can be calculated for the entire stock or individual products/product groups.
Delivery reliability (On Time In Full)
Delivery reliability shows the extent to which deadlines and quantities are met when delivering goods to a recipient. It is made up of two components:
On-time delivery: Are deliveries made on time?
Quantity fulfillment: Is the correct quantity of product delivered in good quality?
The deadlines can be either exact dates or time periods. Specific deadlines are relevant in sectors such as automotive where it is important that the right components are delivered in exactly the right order (just-in-sequence).
Delivery reliability can be expressed with the key figure On Time In Full which is calculated as follows.
Number of timely and complete deliveries / Total number of deliveries
For suppliers, On Time In Full is one of the most important KPIs, as delivery reliability has a significant impact on the company’s reputation and therefore the orders received.
Implementation
Recording and visualization of production metrics
Once a company has identified suitable production metrics or KPIs, they need to be measured or calculated at regular intervals.
The calculation of more complex KPIs such as OEE requires, among other things, the collection of (machine) data from the field level. Ideally, the associated processes should be automated and standardized as far as possible.
The effective visualization of metrics also plays an important role. In order to make data-driven decisions and react immediately to events, data needs to be accessible to decision-makers at all times (ideally in real-time).
The correct presentation of production KPIs helps to identify trends or problems at a glance and localize causes. Trend lines, color indicators and similar design elements are often used for this purpose.

The proper visualization of production data on mobile devices is becoming increasingly relevant. Effective visualizations should be accessible and user-friendly regardless of the utilized devices.
With our cloud platform manubes, we have developed an innovative solution for the real-time visualization of production data and processes. manubes allows companies to automatically gather and structure data from various production-related sources in a secure cloud environment. This data can then be displayed in the form of dynamic and fully responsive real-time dashboards or processed within automated workflows. Using interactive elements such as buttons and forms, teams with the appropriate permissions can interact directly with production processes and control production from the cloud.
As a cloud platform, manubes offers worldwide access on various devices, easy and intuitive operation and a comprehensive security concept.

Seamless Production Monitoring with manubes
manubes allows manufacturers to visualize process parameters, metrics, KPIs and other production data in real-time. Using intuitive design tools, end users can create individualized dashboards with the option to add interfaces for production control.
Try manubes for free
Create a free manubes test account within minutes and try the different features within your personal cloud environment.